Imagine a world where different ways of thinking are celebrated rather than overlooked. Neurodivergent individuals bring unique perspectives and talents to the table, challenging conventional norms and enriching our understanding of human experience. From autism to ADHD, neurodiversity encompasses a range of conditions that redefine what it means to be “normal.”
Understanding Neurodivergence
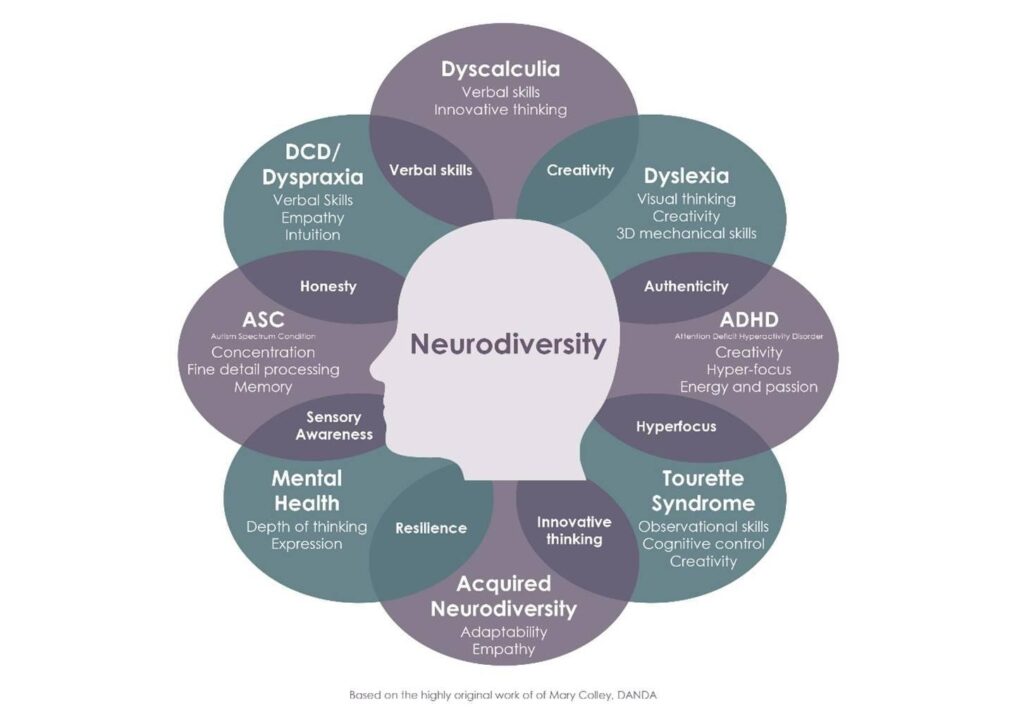
Neurodivergence encompasses a range of differences in brain function and behavior. It includes various cognitive variations that contribute to unique perspectives and experiences, enriching our understanding of humanity.
Definition of Neurodivergent
Neurodivergent refers to individuals whose neurological development and functioning diverge from what is considered typical. This diversity includes conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, and others. These differences are not deficits; they represent distinct ways of processing information and interacting with the world.
Common Neurodivergent Conditions
Several neurodivergent conditions exemplify the rich tapestry of human cognition:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Characterized by challenges in social communication and repetitive behaviors. Individuals may also possess exceptional skills or interests.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Marked by difficulties in maintaining attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. Many people with ADHD exhibit creativity and problem-solving abilities.
- Dyslexia: A learning difference that affects reading skills despite intelligence levels being average or above average. Individuals often excel in verbal skills.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Involves unwanted thoughts leading to repetitive behaviors. Some find their routines help them focus better on tasks.
Recognizing these conditions promotes acceptance and understanding within society. When you embrace neurodiversity, you appreciate diverse talents each individual brings to the table.
The Importance of Neurodiversity
Neurodiversity plays a crucial role in fostering understanding and acceptance in society. Recognizing the strengths and challenges of neurodivergent individuals enhances collective growth.
Benefits of Embracing Neurodiversity
Embracing neurodiversity brings numerous advantages, both socially and economically. For example:
- Innovation: Neurodivergent thinkers often approach problems differently, leading to innovative solutions.
- Enhanced Creativity: Individuals with dyslexia frequently excel in creative fields due to their unique perspective.
- Diverse Workplaces: Companies that prioritize neurodiverse hiring tap into a wider range of skills and ideas.
You might notice how these benefits contribute positively to communities and organizations alike.
Challenges Faced by Neurodivergent Individuals
Despite the many benefits, neurodivergent individuals face specific challenges. Understanding these issues is essential for promoting inclusivity:
- Social Interaction Difficulties: Many autistic individuals experience challenges in social settings, affecting relationships.
- Stigma: Misconceptions about conditions like ADHD or OCD can lead to discrimination.
- Access to Resources: Limited support systems may hinder educational or employment opportunities.
It’s vital to address these obstacles to create an environment where everyone thrives.
Representation in Media and Society
Representation of neurodivergent individuals in media and society significantly impacts public perception. Positive portrayals can foster understanding, while negative stereotypes perpetuate misconceptions.
Positive Portrayals of Neurodivergence
Media often highlights the strengths of neurodivergent characters, showcasing their unique talents and perspectives. For instance:
- “Atypical”: This series depicts an autistic teenager navigating relationships, emphasizing empathy and resilience.
- “Mozart and the Whale”: Based on real-life events, this film illustrates individuals with Asperger’s forming a romantic bond through shared interests.
- “Rain Man”: A classic film that brought attention to autism by portraying a savant’s extraordinary abilities.
These examples promote acceptance, demonstrating that neurodiversity enriches narratives.
Stereotypes and Misconceptions
Despite positive representations, many stereotypes persist around neurodivergent individuals. Common misconceptions include:
- Autistic individuals lack emotions: Many assume people with autism cannot feel or express emotions, which is inaccurate.
- ADHD means hyperactivity only: ADHD encompasses various symptoms, including inattentiveness not always linked to hyperactivity.
- Neurodiversity equates to disability: While some may face challenges, many experience strengths that enhance their contributions.
Addressing these misunderstandings helps create a more inclusive environment for all.
Support and Resources for Neurodivergent Individuals
Neurodivergent individuals benefit from various support systems and resources tailored to their unique needs. These supports enhance educational experiences and workplace environments, fostering inclusion.
Educational Support Systems
Educational institutions offer multiple support systems for neurodivergent students. These may include:
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): Customized plans that address specific learning needs.
- 504 Plans: Accommodations ensuring equal access to education without an IEP.
- Assistive Technology: Tools like speech-to-text software aid in communication and learning.
Teachers trained in neurodiversity help create inclusive classrooms by adapting teaching methods. For instance, using visual aids enhances understanding for students with dyslexia or autism. Access to counseling services also provides emotional support, promoting mental well-being.
Workplace Accommodations
In workplaces, accommodations make a significant difference for neurodivergent employees. Examples of effective accommodations include:
- Flexible Work Hours: Allowing adjustments based on productivity patterns.
- Quiet Spaces: Designated areas reduce sensory overload, enhancing focus.
- Clear Communication Channels: Using direct language minimizes misunderstandings.
Employers can foster an inclusive culture by providing training on neurodiversity awareness. This approach helps colleagues understand diverse working styles while promoting collaboration. By implementing these strategies, workplaces create environments where neurodivergent individuals thrive alongside their peers.