Have you ever felt like your emotions are on a rollercoaster, swinging from extreme highs to crushing lows? Mood disorders can turn everyday life into a challenging journey, affecting not just your feelings but also your relationships and overall well-being. These conditions encompass a range of issues, including depression and bipolar disorder, each presenting unique symptoms that can be hard to navigate.
Understanding Mood Disorders
Mood disorders create significant emotional instability, affecting your daily life and relationships. These conditions can lead to extreme emotional states, impacting overall well-being.
Definition of Mood Disorders
Mood disorders are mental health conditions characterized by persistent changes in mood. They often involve episodes of depression or mania. You might experience symptoms like sadness, irritability, or an exaggerated sense of euphoria. Recognizing these shifts is crucial for seeking appropriate help.
Types of Mood Disorders
Several types of mood disorders exist, each with unique features:
- Major Depressive Disorder: Characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest in activities once enjoyed.
- Bipolar Disorder: Involves alternating periods of depression and elevated mood (mania), leading to significant lifestyle disruptions.
- Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia): A chronic form of depression lasting for at least two years, often less severe but long-lasting.
- Cyclothymic Disorder: Features numerous periods of hypomanic symptoms and depressive symptoms that last for at least two years.
Understanding these types helps you identify underlying issues and promotes effective treatment strategies.
Symptoms of Mood Disorders
Mood disorders present a variety of symptoms that can greatly affect daily life. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for seeking help and managing the conditions effectively.
Emotional Symptoms
Emotional symptoms often dominate the experience of mood disorders. Individuals may feel persistent sadness or hopelessness, affecting their outlook on life. You might notice:
- Irritability: Frequent frustration over minor issues.
- Loss of interest: A disinterest in activities once enjoyed.
- Feelings of worthlessness: Constant self-doubt or guilt.
These emotional changes can lead to difficulties in relationships and impact overall quality of life.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms also play a significant role in mood disorders. They manifest through various bodily sensations and changes, including:
- Fatigue: Ongoing tiredness despite adequate sleep.
- Sleep disturbances: Insomnia or oversleeping that disrupts routine.
- Changes in appetite: Significant weight loss or gain due to altered eating habits.
Understanding these physical aspects helps you recognize how deeply mood disorders affect not just emotions but also physical health.
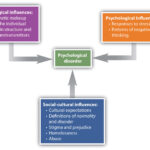
Causes of Mood Disorders
Understanding the causes of mood disorders is essential for effective treatment and management. Several factors contribute to these conditions, ranging from genetic predispositions to environmental influences.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors play a significant role in mood disorders. Research indicates that individuals with a family history of mood disorders face higher risks. For instance:
- Major Depressive Disorder: A first-degree relative with this condition increases your chances significantly.
- Bipolar Disorder: Studies show that if one parent has bipolar disorder, the risk for their child can rise up to 15%.
These statistics highlight the importance of recognizing hereditary patterns when assessing mental health.
Environmental Influences
Environmental influences also contribute to the development of mood disorders. Stressful life events or chronic stressors can trigger episodes, such as:
- Trauma: Experiencing physical or emotional trauma often leads to increased vulnerability.
- Substance Abuse: Drug or alcohol misuse frequently exacerbates existing mood disorders.
- Social Isolation: Lack of support from friends and family may intensify feelings of depression or anxiety.
Recognizing these factors helps you understand potential triggers and seek appropriate interventions effectively.
Treatment Options for Mood Disorders
Various treatment options exist for mood disorders, helping individuals manage symptoms effectively. These approaches include psychotherapy, medications, and lifestyle changes.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy offers valuable support in managing mood disorders. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. Interpersonal therapy assists in improving relationships and communication skills. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) emphasizes emotional regulation and mindfulness techniques. Each type of therapy can provide you with coping strategies tailored to your specific needs.
Medications
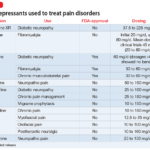
Medications play a crucial role in treating mood disorders. Antidepressants like Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) target serotonin levels, alleviating depressive symptoms. Mood stabilizers such as lithium help control manic episodes in Bipolar Disorder. Atypical antipsychotics may also be prescribed for severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication that suits your situation.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes significantly impact mood disorder management. Regular exercise releases endorphins, enhancing overall well-being. Balanced nutrition supports brain health; foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids—like fish and walnuts—can improve mood stability. Additionally, establishing a consistent sleep schedule promotes better mental health by ensuring adequate rest each night. Incorporating these changes can lead to improved symptom management and quality of life.
The Impact of Mood Disorders on Daily Life
Mood disorders significantly affect daily life in various ways, leading to challenges in personal and professional spheres. Understanding these impacts helps in recognizing the importance of addressing mood disorders effectively.
Personal Relationships
Mood disorders can create barriers in personal relationships. For instance, persistent sadness or irritability may strain interactions with family and friends. You might find yourself withdrawing from social activities that once brought joy, which can lead to feelings of isolation.
Moreover, emotional instability associated with conditions like bipolar disorder causes unpredictable behavior, making it tough for loved ones to understand your needs. This unpredictability often leads to misunderstandings and conflicts, further complicating relationships.
Professional Life
In the workplace, mood disorders impact productivity and job performance. When experiencing fatigue or difficulty concentrating, completing tasks becomes challenging. You might miss deadlines or struggle with collaboration due to emotional fluctuations.
Additionally, absenteeism is common among those managing mood disorders; frequent sick days can raise concerns among coworkers and supervisors about reliability. These factors combined create a work environment that often feels overwhelming rather than supportive, affecting overall career advancement opportunities.
Understanding these impacts emphasizes the necessity for effective management strategies tailored to individual experiences with mood disorders.