Have you ever wondered how our thoughts and behaviors can be influenced by the actions of others? Modeling psychology provides fascinating insights into this phenomenon. It’s a concept that explains how individuals learn and adopt behaviors by observing those around them, whether they’re parents, peers, or even media figures.
Overview of Modeling Psychology
Modeling psychology focuses on how individuals learn behaviors through observation. You see this in various contexts, from childhood to adulthood.
For instance, children often imitate their parents’ actions. If a child observes a parent demonstrating kindness or sharing, they’re likely to replicate that behavior with peers.
In educational settings, students model teachers’ methods. When a teacher uses engaging techniques or positive reinforcement, students adopt those strategies themselves.
Media also plays a significant role. Characters in movies and TV shows can influence viewers’ attitudes and behaviors. For example, when characters display bravery or resilience, audiences may feel inspired to emulate these traits.
Social situations provide another avenue for modeling psychology. In group dynamics, individuals might adjust their behavior based on what others do. This can lead to conformity where people align with the group’s actions even if it contradicts personal beliefs.
Overall, modeling psychology illustrates the powerful impact of observation on learning and behavior adoption across various environments.
Key Concepts in Modeling Psychology
Modeling psychology centers around how you acquire behaviors through observation. This process occurs naturally and influences various aspects of life, ranging from childhood development to adult interactions.
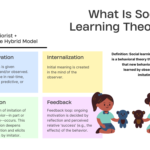
Definition of Modeling
Modeling refers to the process through which you learn behaviors by observing others. It involves imitating actions seen in role models, be they family members, friends, or public figures. For example, a child mimicking a parent’s kindness showcases the essence of modeling. Additionally, it extends beyond direct imitation; you might adopt certain traits or attitudes merely by witnessing them in your environment.
Importance of Modeling in Psychology
The significance of modeling in psychology lies in its impact on learning and behavioral development. It shapes how you navigate social situations and adapt to new environments. Here are key points about its importance:
- Social Learning: You often learn effective communication skills by watching peers interact.
- Behavioral Norms: Observing societal norms helps you understand acceptable behavior within different contexts.
- Emotional Responses: Witnessing how others react emotionally can guide your own responses during similar situations.
Examples of Modeling Psychology
Modeling psychology manifests in various real-world scenarios. Here are two prominent examples that illustrate its application.
Social Learning Theory
Social Learning Theory emphasizes learning through observation and imitation. For instance, children often learn social behaviors by watching their parents or peers. If a child sees a sibling sharing toys, they’re likely to imitate this behavior. This demonstrates how modeling shapes interpersonal skills and promotes prosocial behavior.
Another example can be found in educational settings. Teachers who display enthusiasm during lessons encourage students to engage actively. When students observe positive reinforcement from their teachers, they adopt similar attitudes towards learning.
Behavioral Modeling in Therapy
Behavioral modeling plays a crucial role in therapeutic contexts. Therapists often demonstrate coping strategies for clients facing anxiety or phobias. For instance, when dealing with social anxiety, a therapist might model appropriate social interactions during role-playing exercises. Clients gain confidence by observing effective techniques firsthand.
Additionally, group therapy sessions utilize modeling as participants share personal experiences and coping methods. Hearing others discuss their challenges fosters understanding and encourages the adoption of new strategies for overcoming difficulties you may face in life.
Applications of Modeling Psychology
Modeling psychology has significant applications across various fields, influencing how behaviors are learned and adopted. Here are two key areas where modeling plays a crucial role.
Education and Learning Environments
In educational settings, modeling shapes student behavior and learning outcomes. Teachers who demonstrate enthusiasm can inspire students to engage more actively in class. For instance:
- Peer Interaction: Students learn collaboration skills by observing classmates working together.
- Role Models: Effective communication techniques often emerge when students see teachers using clear instructions and positive reinforcement.
- Classroom Management: Educators displaying patience encourage similar responses from their students.
These examples illustrate how modeling can enhance the overall educational experience.
Workplace Training and Development
Modeling psychology also applies to workplace training programs, impacting skill development and organizational culture. Employees often learn best by observing their peers or supervisors. Consider these instances:
- On-the-job Training: New hires observe experienced colleagues demonstrating best practices for specific tasks.
- Leadership Behavior: Managers who model transparent communication foster an environment of trust among team members.
- Feedback Mechanisms: When employees witness constructive feedback being given, they feel encouraged to share insights openly.
Such practices help create a cohesive work environment that promotes continuous learning and improvement.