Have you ever wondered how certain behaviors are learned and reinforced? Modeling behavior examples play a crucial role in shaping our actions and responses. From children mimicking their parents to employees adopting workplace norms, the impact of modeling is everywhere.
Understanding Modeling Behavior
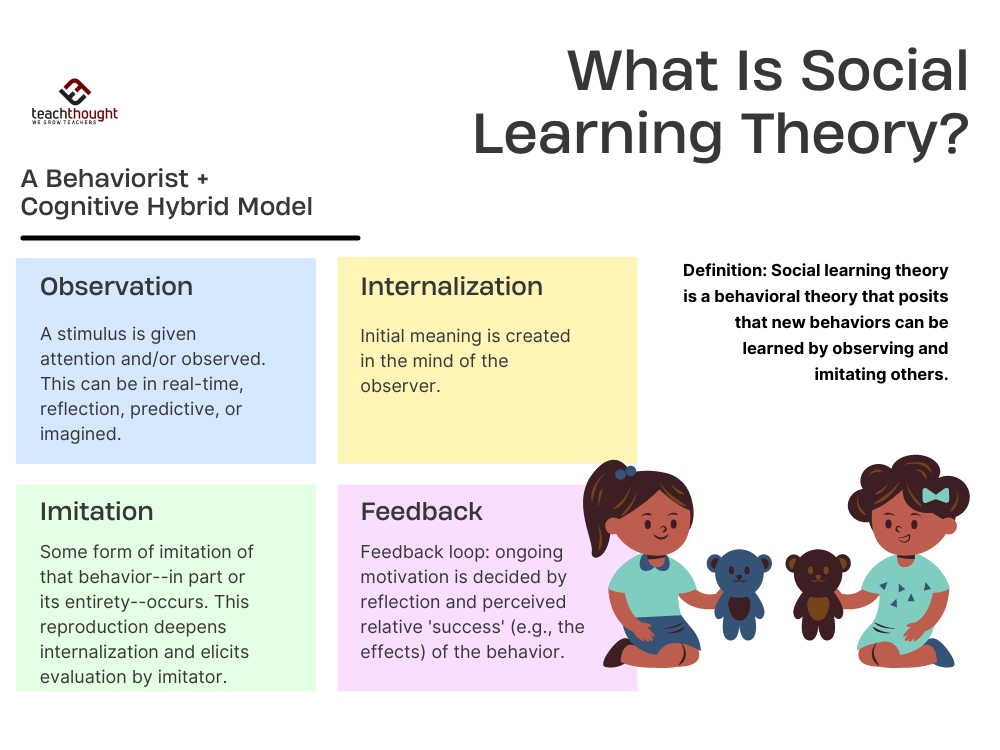
Modeling behavior plays a crucial role in how individuals learn and adapt to their environments. By observing others, people often replicate actions, attitudes, and responses. This process greatly influences personal development and social interactions.
Definition of Modeling Behavior
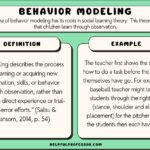
Modeling behavior refers to the act of learning through observation. When you see someone perform a task or exhibit a certain attitude, you might mimic that action. For example:
- Children imitating parents: Kids often copy their parents’ habits, from saying “please” and “thank you” to daily routines.
- Employees following managers: In workplaces, staff may adopt behaviors seen in successful colleagues or supervisors.
These examples show how influential modeling can be in shaping individual conduct.
Importance of Modeling Behavior
Understanding the significance of modeling behavior is essential for fostering positive environments. Here are key reasons why it matters:
- Promotes Learning: Observational learning helps individuals acquire new skills without direct instruction.
- Shapes Social Norms: People often conform to group behaviors observed within their community or workplace.
- Encourages Positive Conduct: Role models can inspire others to adopt constructive habits and attitudes.
Ultimately, recognizing these aspects encourages effective strategies for teaching and influencing behavior across various settings.
Types of Modeling Behavior
Modeling behavior occurs in various forms, each playing a unique role in learning and social interaction. Here are two primary types of modeling behavior that illustrate how people learn from observing others.
Direct Modeling
Direct modeling involves straightforward imitation. You see someone perform a task or exhibit a behavior, then you replicate it. This process is common among children who mimic their parents or peers. For example:
- Children copying parents: When kids observe their parents cooking, they often want to try it themselves.
- Employees imitating colleagues: In the workplace, new hires frequently follow experienced coworkers to learn best practices.
Such examples highlight how direct modeling effectively conveys skills and behaviors across generations and settings.
Indirect Modeling
Indirect modeling relies on observation without direct imitation. Instead of replicating an action verbatim, you absorb attitudes and values through watching others. This form can influence your decisions significantly. Some scenarios include:
- Media influences: Watching characters in shows or movies can shape your perceptions about relationships and lifestyle choices.
- Peer dynamics: Observing classmates handle stress may affect how you cope during challenging times.
These indirect experiences contribute to shaping your beliefs, making them essential for personal development and social understanding.
Real-Life Examples of Modeling Behavior
Modeling behavior manifests in everyday situations, demonstrating its vital role in shaping actions and attitudes. Here are some specific examples across different environments.
Family Settings
In family dynamics, children often emulate their parents’ behaviors. For instance, if a parent shows kindness by helping neighbors, the child is likely to adopt similar helpfulness. Additionally, strong communication skills modeled by parents can lead to better social interactions for their kids. When siblings resolve conflicts constructively, younger ones learn effective conflict resolution strategies as well.
Educational Environments
In schools, teachers significantly influence students through modeling behavior. For example, when educators demonstrate enthusiasm for learning, it tends to inspire similar excitement among students. Also, demonstrating respect during classroom discussions encourages students to engage respectfully with peers. Furthermore, group activities where collaboration is emphasized teach teamwork and compromise effectively through direct observation.
Workplace Situations
In professional settings, employees often look up to their managers as role models. If a manager prioritizes transparency and feedback in communications, team members are likely to mirror that openness in their interactions. Similarly, adhering to punctuality sets a standard within the workplace—when one person consistently arrives on time for meetings or deadlines others tend to follow suit as well. Peer behavior also plays a significant role; observing colleagues who maintain high standards of ethics influences overall workplace culture positively.
Benefits of Modeling Behavior Examples
Modeling behavior examples offer several advantages in various contexts, enhancing learning and social interactions. Understanding these benefits helps you apply modeling effectively in everyday situations.
Skill Development
Skill development occurs when you observe and imitate others’ behaviors. For instance, a child might learn to tie their shoes by watching a parent demonstrate the process. In professional settings, employees often acquire new skills by observing experienced colleagues. This direct exposure facilitates faster learning and application of necessary skills.
Social Learning
Social learning thrives on the principles of observation and imitation. When you see peers demonstrating effective communication, it encourages similar behaviors in your interactions. For example, students may adopt respectful dialogue patterns after seeing teachers engage positively with one another. Such environments foster collaboration and understanding among individuals.
Emotional Growth
Emotional growth is significantly influenced by modeling behavior. You can develop empathy by observing how others respond to different situations. Consider someone who witnesses a friend comforting another during distress; this act can inspire compassionate responses in future scenarios. By recognizing emotional cues modeled by others, individuals enhance their ability to navigate complex emotional landscapes effectively.