In the fast-paced world of business, mergers and acquisitions examples can illuminate the strategies that shape entire industries. Have you ever wondered how companies like Disney and Pixar or Facebook and Instagram transformed their markets? These high-profile deals not only redefine competitive landscapes but also showcase innovative approaches to growth.
Overview of Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) significantly impact industries and economies. They often lead to larger market shares, increased efficiencies, and expanded product offerings. Here are some notable examples:
- Disney and Pixar: In 2006, Disney acquired Pixar for $7.4 billion. This merger revitalized Disney’s animation division, resulting in blockbuster hits like “Toy Story 3” and “Frozen.”
- Facebook and Instagram: Facebook bought Instagram in 2012 for approximately $1 billion. This acquisition enhanced Facebook’s social media portfolio, attracting younger users.
- Amazon and Whole Foods: Amazon acquired Whole Foods for $13.7 billion in 2017. This purchase allowed Amazon to enter the grocery sector, integrating online shopping with physical stores.
- Google and YouTube: Google purchased YouTube in 2006 for $1.65 billion. This acquisition positioned Google as a leader in video content distribution.
These M&A transactions illustrate how businesses leverage mergers to achieve strategic goals while reshaping their competitive landscape effectively.
Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) come in various forms, each serving distinct strategic purposes. Understanding these types helps clarify how businesses align their goals through such transactions.
Horizontal Mergers
Horizontal mergers occur between companies operating at the same level in the industry. These firms typically offer similar products or services. For instance, when two competing technology companies merge, they can consolidate resources, reduce competition, and enhance market share. A notable example is the merger between SBC Communications and AT&T in 2005, which created a telecommunications giant with broader service capabilities.
Vertical Mergers
Vertical mergers involve companies at different stages of production within the same industry. This type allows for greater control over supply chains and cost efficiencies. An example is Disney’s acquisition of Pixar, where Disney enhanced its animation capabilities by integrating Pixar’s innovative technologies into its operations. Such mergers often lead to improved product quality and streamlined processes.
Conglomerate Mergers
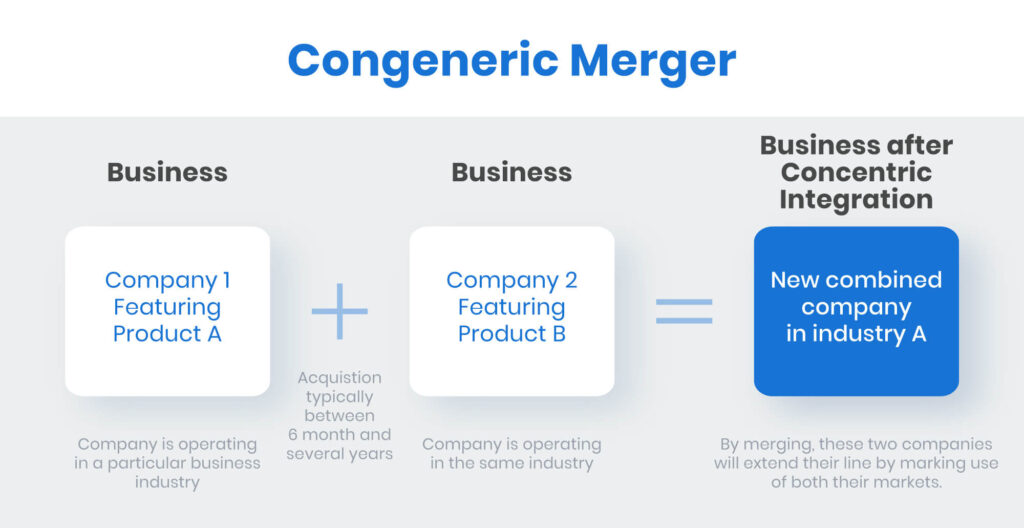
Conglomerate mergers happen when companies from unrelated industries combine. This strategy diversifies business interests and reduces risks associated with market fluctuations. A prime example is General Electric’s acquisition of NBC in 1986, which allowed GE to venture into media while strengthening its portfolio beyond manufacturing. These mergers can foster innovation by leveraging different expertise across sectors.
Notable Mergers and Acquisitions Examples
Mergers and acquisitions significantly reshape industries. Here are some notable examples across various sectors that illustrate their impact.
Tech Industry
Facebook’s acquisition of Instagram in 2012 transformed the social media landscape. Facebook recognized the potential of Instagram’s photo-sharing platform, leading to exponential growth in user engagement. Another example is Google’s purchase of YouTube in 2006. This deal not only provided Google with a dominant position in video sharing but also expanded its advertising capabilities.
Healthcare Sector
In healthcare, CVS Health’s acquisition of Aetna in 2018 marked a significant consolidation effort aimed at integrating health services and insurance. This merger enables CVS to offer a more comprehensive suite of healthcare solutions, enhancing patient access to services. Similarly, Bristol-Myers Squibb’s acquisition of Celgene in 2019 strengthened its oncology portfolio, allowing for increased innovation in cancer treatment options.
Retail Sector
The retail sector saw major shifts with Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods Market in 2017. This move enabled Amazon to enter the grocery industry while enhancing its delivery capabilities. Moreover, The Home Depot’s purchase of The Company Store in 2025 allowed it to expand its home decor offerings, further solidifying its position as a leader in home improvement products.
Factors Influencing Mergers and Acquisitions
Numerous factors influence mergers and acquisitions, shaping decisions that companies make to achieve growth and competitive advantage.
Market Trends
Market trends play a crucial role in driving M&A activity. Companies often pursue acquisitions to stay ahead of industry changes. For instance, the rise of digital technology prompted many traditional retailers to acquire tech firms for e-commerce capabilities.
- Increased competition: As new players enter markets, established firms look to merge or acquire competitors.
- Consumer preferences: Shifts in consumer behavior push companies to adapt quickly through strategic partnerships.
- Technological advancements: Innovations can prompt firms to seek out tech-savvy partners.
By aligning with market trends, businesses enhance their adaptability and secure their positions within their industries.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment significantly impacts the feasibility and success of M&A transactions. Laws and regulations can either facilitate or hinder these deals.
- Antitrust laws: Governments monitor M&A activity to prevent monopolies, requiring companies to demonstrate benefits for consumers.
- Foreign investment regulations: Restrictions may apply when foreign entities seek domestic acquisitions, impacting global strategies.
- Industry-specific regulations: Certain sectors face stricter guidelines that complicate merger processes.
Understanding the regulatory landscape is essential for navigating mergers and acquisitions effectively. Compliance ensures smoother transitions and mitigates legal risks associated with these transactions.