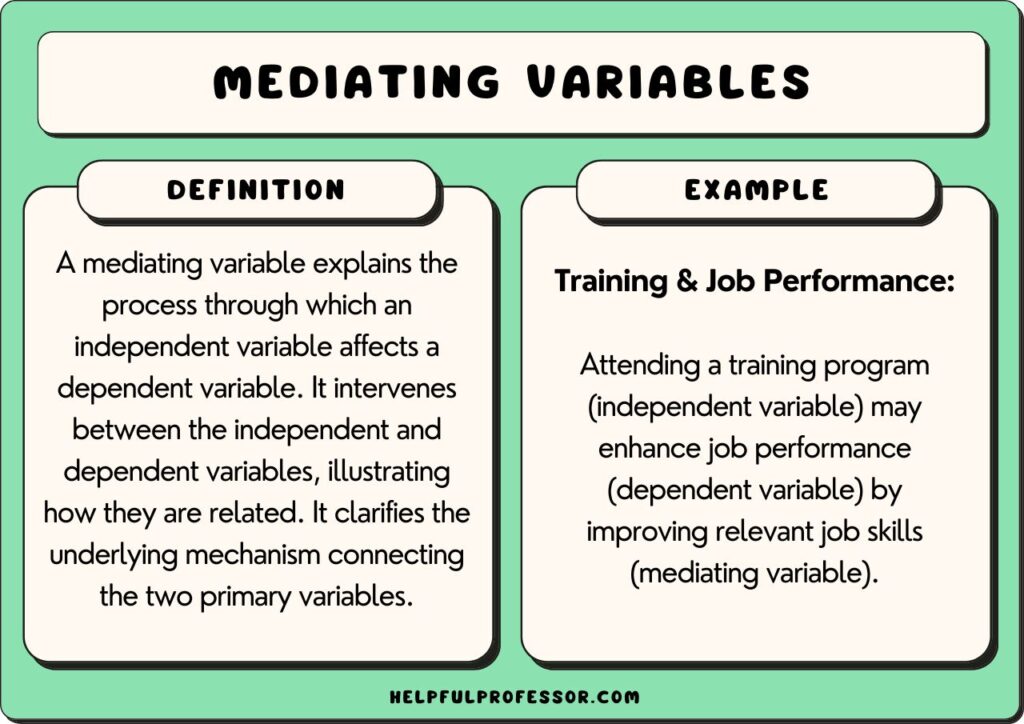
Understanding the concept of a mediating variable can transform how you analyze relationships in your research. Have you ever wondered why certain factors influence outcomes in unexpected ways? A mediating variable acts as a bridge, explaining how or why two variables are connected.
Understanding Mediating Variables
Mediating variables play a crucial role in research analysis by clarifying the relationship between independent and dependent variables. They help uncover unexpected influences that might affect outcomes.
Definition and Importance
A mediating variable explains how or why two variables are related. For example, consider the relationship between education level and income. Here, job skills serve as a mediating variable, demonstrating how education leads to better job opportunities, which subsequently increase income. This connection highlights the importance of mediating variables in understanding complex relationships.
Distinction from Other Variables
Mediating variables differ from moderating and confounding variables. While mediators explain the process behind a relationship, moderating variables influence the strength or direction of that relationship. Confounding variables distort true associations by being linked to both independent and dependent variables. Recognizing these distinctions helps clarify research findings:
- Mediators: Explain mechanisms (e.g., self-esteem affecting health).
- Moderators: Impact effects (e.g., age altering stress levels).
- Confounders: Mislead results (e.g., socioeconomic status affecting both diet and health).
Understanding these differences enhances your ability to analyze data accurately.
Types of Mediating Variables
Mediating variables can be classified into different types based on their function and role in research. Understanding these distinctions enhances the clarity of data analysis.
Direct vs. Indirect Mediators
Direct mediators act as a straightforward link between two variables. For example, consider how stress might directly mediate the relationship between workload and employee performance. Increased workload raises stress levels, which in turn affects performance.
Indirect mediators involve multiple steps or factors. In this case, education level could indirectly influence job satisfaction through increased income. Here, income serves as an indirect mediator that connects education to job satisfaction.
Examples in Research
Examples illustrate how mediating variables operate within various contexts:
- Health Studies: A study might find that physical activity mediates the relationship between diet quality and weight loss.
- Education Research: Academic motivation often acts as a mediator between parental involvement and student achievement.
- Psychology: Emotional intelligence can mediate the effects of personality traits on interpersonal relationships.
These examples emphasize how mediating variables clarify complex relationships across different disciplines.
Role of Mediating Variables in Research
Mediating variables significantly enhance the understanding of complex relationships within research. They clarify how two variables interact, providing insight into underlying mechanisms. This section explores their roles in enhancing research validity and facilitating causal inferences.
Enhancing Research Validity
Mediating variables improve research validity by clarifying the connections between independent and dependent variables. For example, consider a study examining how physical activity affects mental health. Here, social support acts as a mediating variable that explains why increased exercise leads to improved well-being. By identifying this mediator, researchers can draw more accurate conclusions about the relationship.
Additionally, strong mediating variables allow for deeper analysis, helping researchers avoid misleading results caused by confounding factors. For instance, when studying educational outcomes influenced by parental involvement, student motivation serves as a mediator that highlights how supportive parents impact academic success.
Facilitating Causal Inferences
Mediating variables also facilitate causal inferences by demonstrating the processes through which one variable influences another. When you analyze marketing strategies on consumer behavior, brand loyalty can be a mediating variable. It shows that effective advertising not only attracts customers but also fosters long-term loyalty that drives repeat purchases.
Moreover, understanding these mediation effects helps establish clearer cause-and-effect relationships. Take healthcare studies; if researchers find that dietary changes mediate weight loss and improved health outcomes, it becomes easier to advocate for dietary interventions as effective treatments for obesity-related conditions.
Recognizing the role of mediating variables is essential for producing robust research findings and drawing valid conclusions across various fields.
Methods for Analyzing Mediating Variables
Analyzing mediating variables involves various statistical techniques and software tools that enhance understanding of relationships between variables.
Statistical Techniques
Several statistical techniques effectively analyze mediating variables:
- Regression Analysis: This technique assesses the relationship between independent, dependent, and mediating variables. For instance, regression can show how stress levels mediate the effect of workload on employee performance.
- Path Analysis: Path analysis visualizes direct and indirect relationships among variables. It helps in identifying pathways through which a mediator operates, such as examining how education impacts income through job skills.
- Structural Equation Modeling (SEM): SEM enables simultaneous evaluation of multiple relationships. You might use SEM to explore how social support influences mental health by affecting physical activity levels.
Common Software for Analysis
Various software programs facilitate the analysis of mediating variables:
- SPSS: Widely used for its user-friendly interface, SPSS provides tools for regression analysis and path analysis to examine mediation effects.
- R: This open-source programming language offers advanced statistical capabilities. Packages like ‘lavaan’ allow you to conduct structural equation modeling easily.
- Mplus: Known for handling complex models, Mplus specializes in latent variable modeling, making it ideal for analyzing mediation in intricate datasets.
Understanding these methods and tools aids your ability to analyze mediating variables effectively in research contexts.