Every product you use daily has gone through a complex journey before reaching your hands. The manufacturing process is the backbone of this journey, transforming raw materials into finished goods. But have you ever wondered how that transformation happens?
In this article, you’ll explore various examples of manufacturing processes that shape industries worldwide. From traditional methods like handcrafting to cutting-edge techniques such as 3D printing, each approach offers unique advantages and challenges. Understanding these processes not only enhances your knowledge but also highlights the innovation driving today’s economy.
Overview Of Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process involves several key stages that transform raw materials into finished products. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring quality and efficiency.
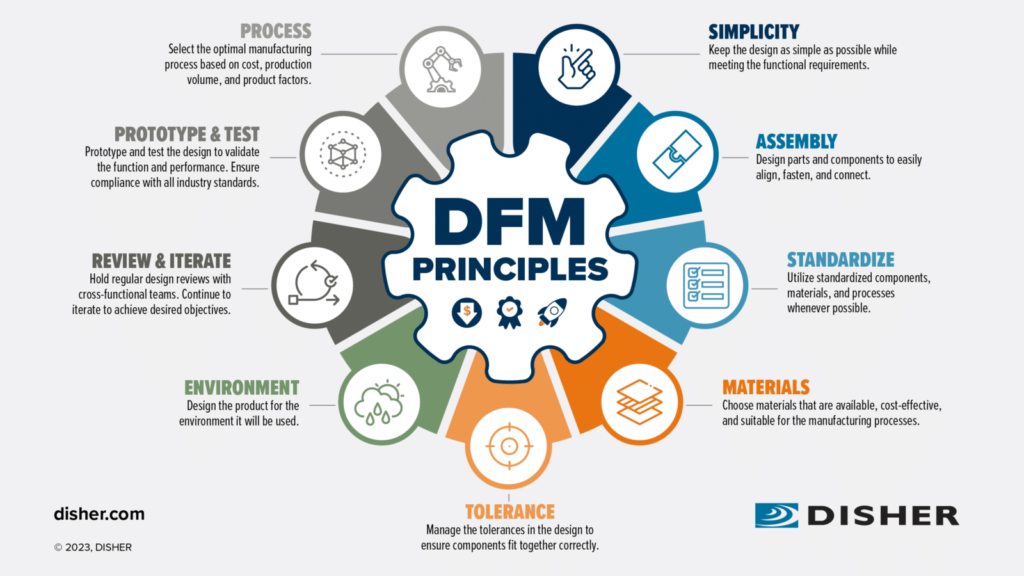
- Design: The journey begins with product design. Engineers and designers collaborate to create detailed specifications, considering functionality, aesthetics, and manufacturability.
- Prototyping: After design approval, prototyping takes place. This step helps identify potential flaws in the product before mass production starts.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials is essential for durability and performance. Manufacturers consider factors like cost, availability, and sustainability when selecting materials.
- Production Planning: Effective production planning determines how resources will be allocated throughout the manufacturing process. It includes scheduling machinery use and workforce assignments.
- Manufacturing Techniques: Several techniques exist within the manufacturing process:
- Traditional Methods: Such as machining or molding.
- Modern Techniques: Including 3D printing or CNC (computer numerical control) machining.
- Quality Control: During production, quality control checks ensure that products meet established standards. This step often involves testing samples from each batch for defects.
- Assembly: In this phase, individual components come together to form the final product. Assembly lines streamline this process for increased efficiency.
- Packaging and Shipping: Once assembled, products undergo packaging to protect them during transportation and storage before reaching consumers.
Each of these stages contributes significantly to delivering high-quality goods efficiently while meeting market demands effectively.
Key Stages In Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process involves several key stages that transform raw materials into finished products. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring quality and efficiency.
Design And Prototyping
Design is the foundation of any product. It defines functionality, aesthetics, and user experience. For example, companies like Apple invest heavily in design to create innovative products that stand out. Prototyping follows design; it allows for testing concepts before mass production. Engineers often use 3D printing to create prototypes quickly and cost-effectively, enabling rapid iteration based on feedback.
Material Selection
Material selection significantly impacts product performance and costs. Manufacturers evaluate factors such as durability, weight, and cost when choosing materials. For instance, aerospace companies often use lightweight composites to enhance fuel efficiency. Conversely, furniture manufacturers may choose solid wood for its strength and aesthetic appeal. This decision directly influences the final product’s quality and marketability.
Production Planning
Production planning outlines how resources are allocated throughout the manufacturing process. It includes scheduling machinery usage, labor assignments, and inventory management. Efficient production planning can reduce waste and increase productivity. For example, automotive manufacturers utilize Just-In-Time (JIT) strategies to minimize stock levels while ensuring parts arrive precisely when needed—this approach optimizes cash flow while maintaining smooth operations.
Types Of Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing processes vary significantly based on the nature of products being produced. Understanding these types helps in choosing the right method for specific needs.
Discrete Manufacturing
Discrete manufacturing involves producing distinct items that can be counted, touched, or seen. Examples include:
- Automobiles: Each car is a separate unit with unique specifications.
- Electronics: Products like smartphones and computers are assembled from various components.
- Furniture: Items such as chairs and tables are crafted individually.
In this process, you often see assembly lines where individual parts come together to form a complete product.
Process Manufacturing
Process manufacturing focuses on producing goods in bulk through chemical or physical processes. Common examples include:
- Food and Beverage: Companies like Coca-Cola manufacture soft drinks using large-scale mixing and bottling techniques.
- Pharmaceuticals: Businesses produce medications through precise chemical formulations.
- Plastics: Manufacturers create plastic materials through continuous extrusion processes.
This type of manufacturing typically results in products that cannot be easily separated into individual units after production.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer, allowing for complex designs and customization. Key examples include:
- 3D Printing: Used in prototyping for industries like aerospace; companies can rapidly create models to test designs.
- Medical Devices: Custom prosthetics are made to fit patients perfectly through additive methods.
- Jewelry Production: Unique pieces are crafted using 3D technologies to achieve intricate patterns.
You’ll find that this innovative approach reduces waste compared to traditional subtractive methods while enabling personalized solutions.
Importance Of Quality Control In Manufacturing Process
Quality control plays a vital role in the manufacturing process. Strong quality control measures ensure that products meet required specifications, which ultimately leads to customer satisfaction. Without these measures, defects can slip through unnoticed, impacting brand reputation and profitability.
For instance, in the automotive industry, companies like Toyota implement rigorous testing protocols. They conduct crash tests and durability assessments to confirm vehicle safety and performance before release. This attention to detail prevents costly recalls and enhances consumer trust.
Similarly, in electronics manufacturing, companies such as Samsung focus on quality assurance at every stage. They perform extensive inspections on components like semiconductors before assembling devices. Such proactive steps minimize failures and ensure high functionality of smartphones and other gadgets.
In the food processing sector, organizations like Nestlé employ strict hygiene standards throughout production lines. Regular checks for contaminants or improper storage conditions help maintain product integrity and safety for consumers. This dedication not only protects public health but also boosts brand loyalty.
Additionally, pharmaceutical manufacturers adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). These regulations require consistent monitoring of processes and environments where drugs are produced. Ensuring products are safe and effective is critical in this highly regulated industry.
Overall, implementing strong quality control systems significantly reduces waste while optimizing resource use. You’ll find that businesses prioritizing these practices often outperform competitors who overlook them.